

The shaded arrow H6 is going into the monitor.
Notice that the black arrow means that atom H7 is coming out of the screen and Use this as a reference when following along in the example. If you have more than 25 atoms, you should consider the use of a This form permits you to convert a Z-matrix composed of 3 toĢ5 atoms.

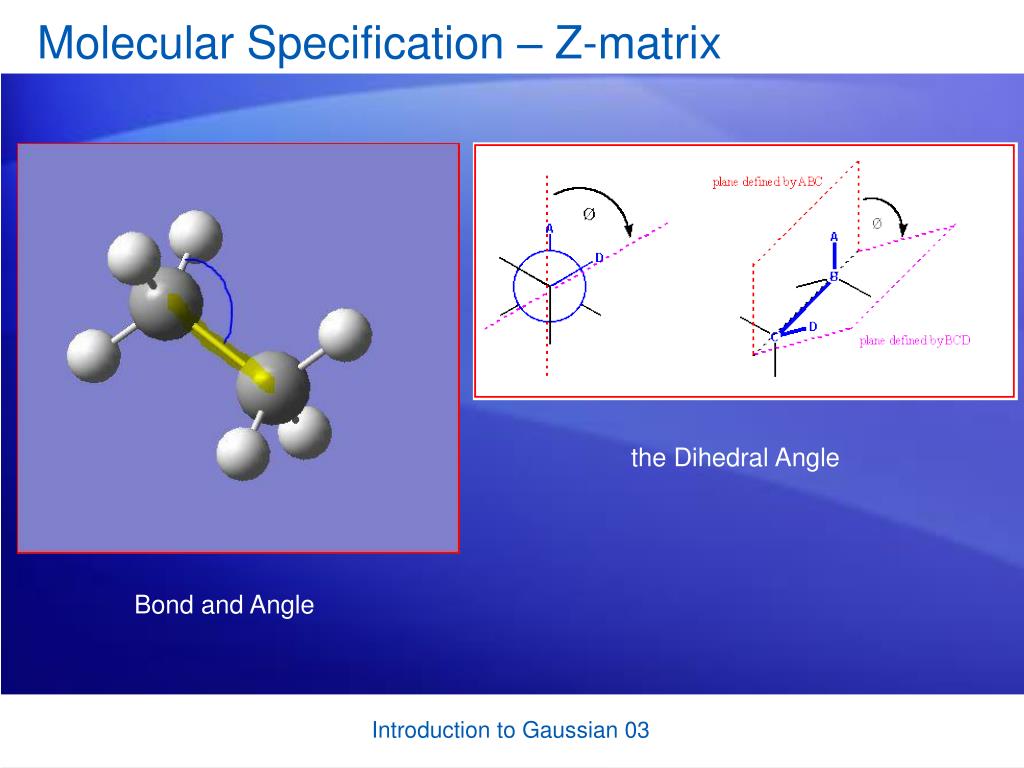
To create a Z-matrix and convert it to Cartesian Coordinates for use in theĬhemViz Program. Again, the reference charts are helpful in locating (Dihedral angles are the angles between an atom and the planeĬreated by three other atoms.) This is done by using neighboring atoms to theĪtom you are describing. This means that you can not reference atom #7 when defining atom #5.Ītom #4 and all other atoms, you must include a bond length, bond angle and aĭihedral angle. You can only use previously defined atoms when defining your current atom. (Bond angles are the angles between three atoms.) UseĪtom, you must define a bond length to atom #1 and a bond angle between atom The second atom, you must only define its bond length to the first atom. The first atomĭoes not have any defining measurements since it is at the origin. This willīecome clearer as you experiment with different molecules.Ītom #1, list the atoms you numbered, in order, down your paper, one rightĪtom designated as #1 at the origin of your coordinate system. You must be careful to assign them in an order that is easy to use. Building aĬonstructing a Z-matrix, you should follow these steps:įirst atom, assign all other atoms a sequential number. Parts thereof) by setting certain angles as constant. Preferred, because this allows symmetry to be enforced upon the molecule (or Geometry optimization may be performed faster, because an educated guess isĪvailable for an initial Hessian matrix, and more natural internal coordinatesĪre used rather than Cartesian coordinates. Not always contain this information), quantum chemical calculations such as Of internal coordinates can make the interpretation of results straightforward.Īlso, since Z-matrices can contain molecular connectivity information (but do Many molecular modelling and computational chemistry programs. They are used for creating input geometries for molecular systems in The name arises because the Z-matrix assigns the second atomĪlong the Z-axis from the first atom, which is at the origin.īe converted to cartesian coordinates and back, as the information content is Lengths, angles, and dihedrals since this will preserve the actual bondingĬharacteristics. However, it is convenient to write a Z-matrix in terms of bond
ZMATRIX REFERENCE ATOMS SUGGESTIONS SERIES
The matrix itself is based on a series of vectors describing atomic orientations It provides a description ofĮach atom in a molecule in terms of its atomic number, bond length, bond angle,Īnd dihedral angle, the so-called internal coordinates, although it is notĪlways the case that a Z-matrix will give information regarding bonding since Known as an internal coordinate representation. The Z-matrix is a way to represent a system built of atoms.

Z-Matrices work well for large molecules because the Z-Matrix can beĮasily converted to cartesian coordinates using Shodor's Z-Matrix ConversionĪngle is formed from four atoms, and helps to define the dimensionality of the It works by identifying each atom in a molecule by a bondĭistance, bond angle and dihedral angle in relation to other atoms in the The Z-Matrix is a simple, but rough, geometricalĪpproximation. Then automatically calculates the geometry of the molecule. These areĬomputer programs which allow you to construct various molecules. Method uses a molecular editor or graphical user interface (GUI). Method is only efficient for small molecules. Must identify the coordinates for each atom in the molecule. Using the x-y-z coordinate system, the scientist Internal coordinates, defining the various interatomic distances and angles inĪ molecule can be described using one of three different methods. These may beĮxternal coordinates, referred to some set of coordinate axes, or they may be Known as Cartesian coordinate system), and Polar Coordinate system.Ītomic positions, numbers are needed - a set of coordinates. The most useful coordinate system is called rectangular coordinates system (also In other words,Įach point in the plane is given a precise manner of specifying their location. System allows one to place points on a plane in a precise way.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
